Case 04: Water - Three Reservoir Problem
Reference: Hydraulics of Pipeline Systems, 2000, CRC Press LLC, Bruce E. Larock, Rowland W. Jeppson, Gary Z. Watters, Page 26, Example problem 2.7
Pipe Flow Expert File: Case_04_Water_Three_Reservoir_Problem.pfe
Problem Description:
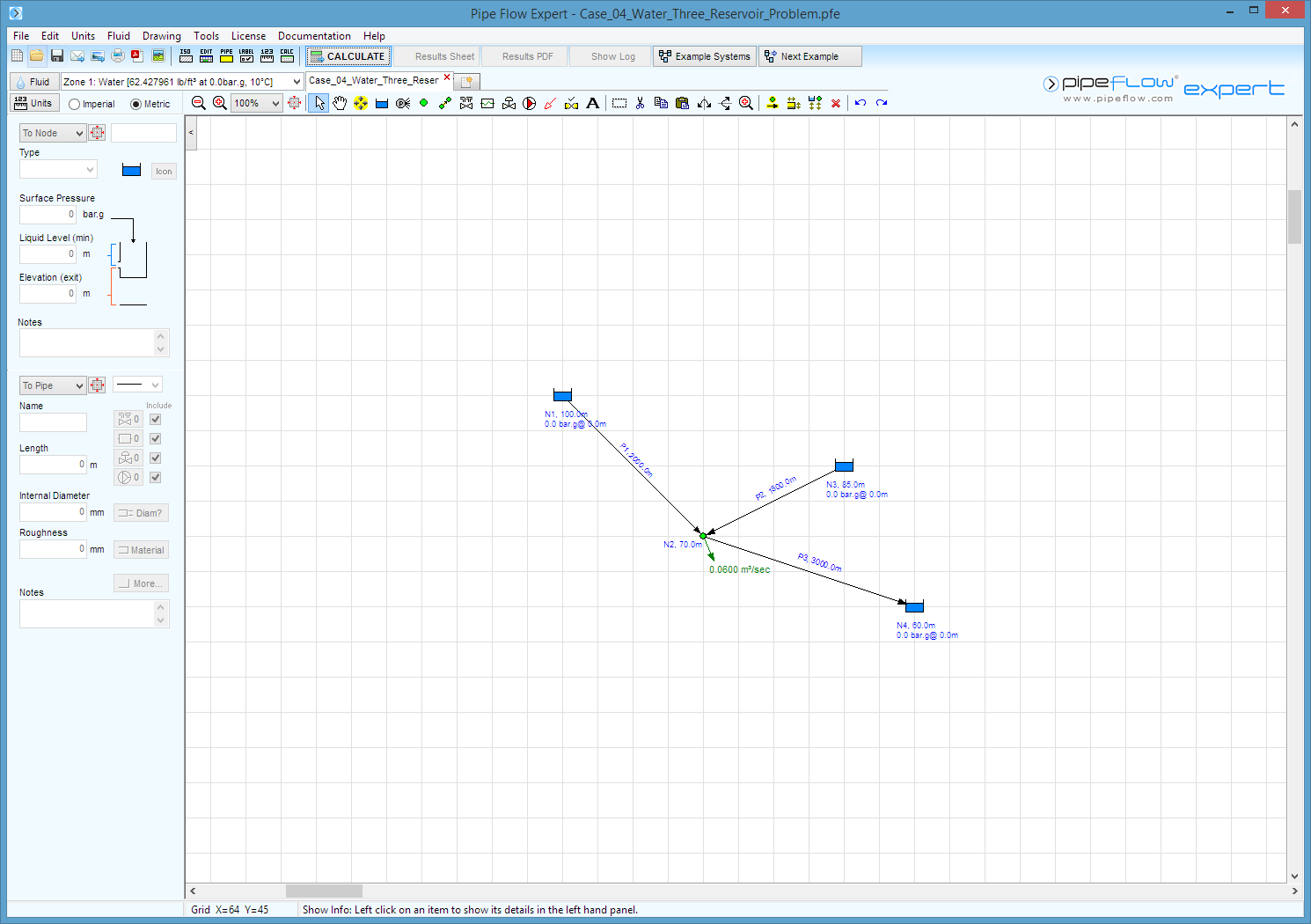
Three water reservoirs are connected by three pipes.
The water surface elevations of the reservoirs are 100 m, 85 m and 60 m.
There is an external demand of 0.06 m³/s at the common junction of the pipes.
The pipe from the high reservoir to the common junction is 2000 m long and has an internal diameter of 300 mm.
The pipe from the middle reservoir to the common junction is 1500 m long and has an internal diameter of 250 mm
The pipe from the common junction to the low reservoir is 3000 m long and has an internal diameter of 250 mm.
The elevation of the common junction is unspecified.
All pipes have an internal roughness of 0.5 mm.
Calculate the flow rate leaving or entering each reservoir.
Fluid Data: Water at 10° C.
Result Comparison:
|
Data Item |
Published data |
Pipe Flow Expert |
|
Flow rate leaving highest reservoir (m³/s) |
0.1023 |
0.1022 |
|
Flow rate leaving middle reservoir (m³/s) |
0.0200 |
0.0200 |
|
Outflow from Common Junction (m³/s) |
0.0600 |
0.0600 |
|
Flow rate entering lowest reservoir (m³/s) |
0.0622 |
0.0622 |
Commentary:
The published data and the calculated results compare well.

