Case 01: Mass Flow of Air
Reference: Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulics, 3rd Ed, 1994, McGraw-Hill; R. V. Giles, J. B. Evett PhD, C. Liu page 237, Example 11.1
Pipe Flow Expert File: Case_01_Mass_Flow_Air.pfe
Problem Description:
Find the mass flow rate of air flowing isothermally through a 6-inch diameter pipe, at 65 °F, where the inlet pressure is 82 psi absolute and the pressure at a distance of 550 feet downstream is 65 psi absolute.
The pipe surface is smooth (the problem specifies an assumed friction factor of 0.0095).
The calculation method used for the published data was the Complete Isothermal Flow equation.
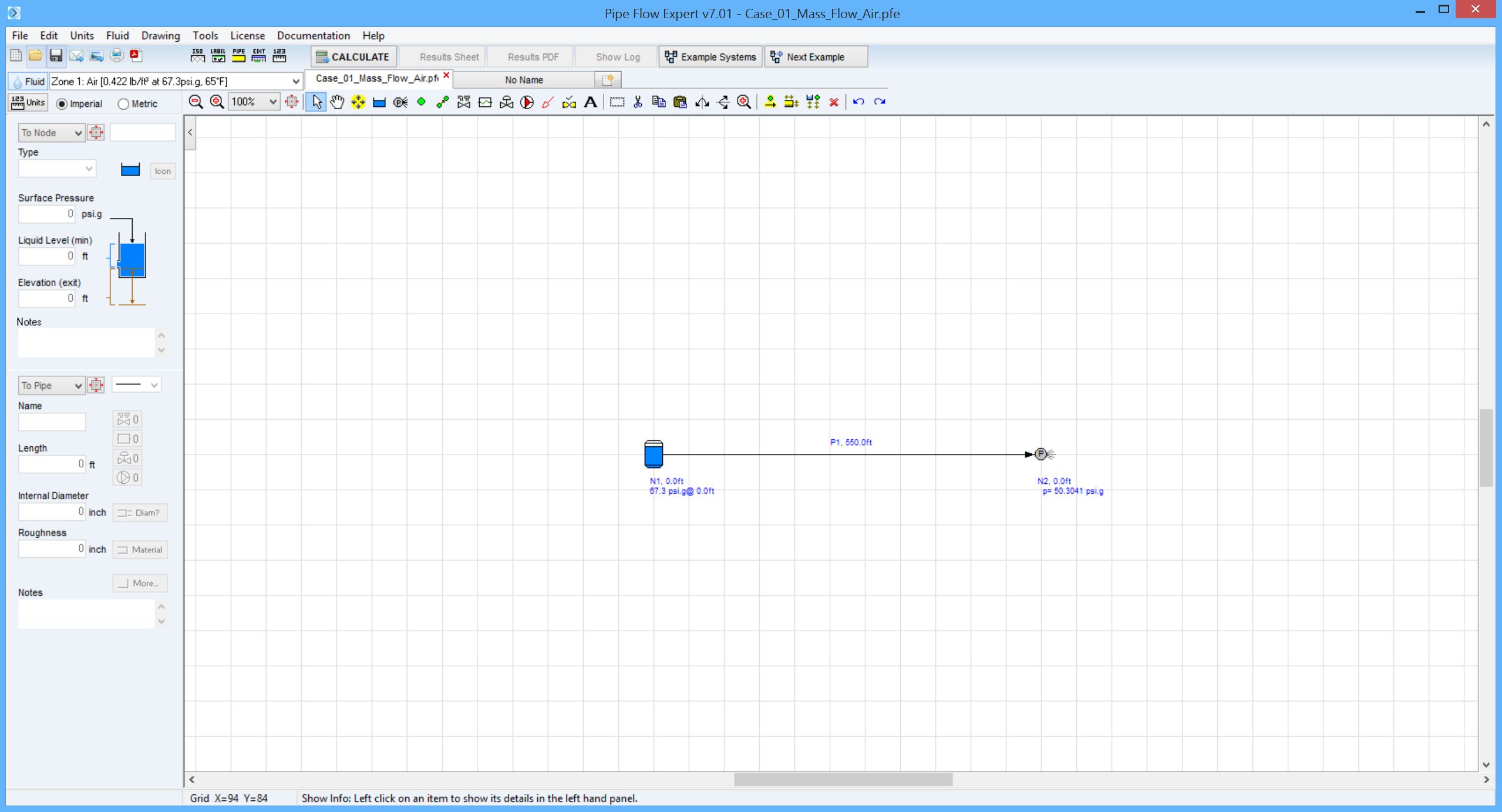
Pipe Flow Expert Parameters:
Fluid Data: Air at 65 °F, 0.0 psi.g, viscosity 0.0181 centipoise.
Pipe Data: Roughness 0.000001 inches (friction factor = 0.00973).
Calculation Method: Complete Isothermal Flow equation, Node Adjust Method.
Standard Atmospheric Model: 68°F, 14.696 psi.
Gas Physical Model: Ideal Gas Law.
Result Comparison:
|
Data Item |
Published data |
Pipe Flow Expert |
|
Mass Flow (lb/sec) |
14.5 |
14.38 |
Commentary:
The published data and the calculated results compare well.
The published data may have used some rounded numbers in the calculation.
The pipe roughness value set in Pipe Flow Expert is very low (much lower than any of the common pipe materials), which is intended to simulate the “smooth” pipe that was used in the published literature (friction factor of 0.0095).

