Case 02: Air Pipeline Pressure Loss
Reference: Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulics, 3rd Ed, 1994, McGraw-Hill; R. V. Giles, J. B. Evett PhD, C. Liu page 238, Example 11.2
Pipe Flow Expert File: Case_02_Air_Pipeline_Pressure_Loss.pfe
Problem Description:
Air at 18 °C flows isothermally through a 300 mm diameter pipe at a flow rate of 0.450 kN/s (equivalent to 45.887 kg/s). The pipe is smooth (friction factor = 0.0080).
If the pressure at the entry point is 550 kPa, find the pressure at a point 200 m downstream.
The calculation method used for the published data was the Complete Isothermal equation.
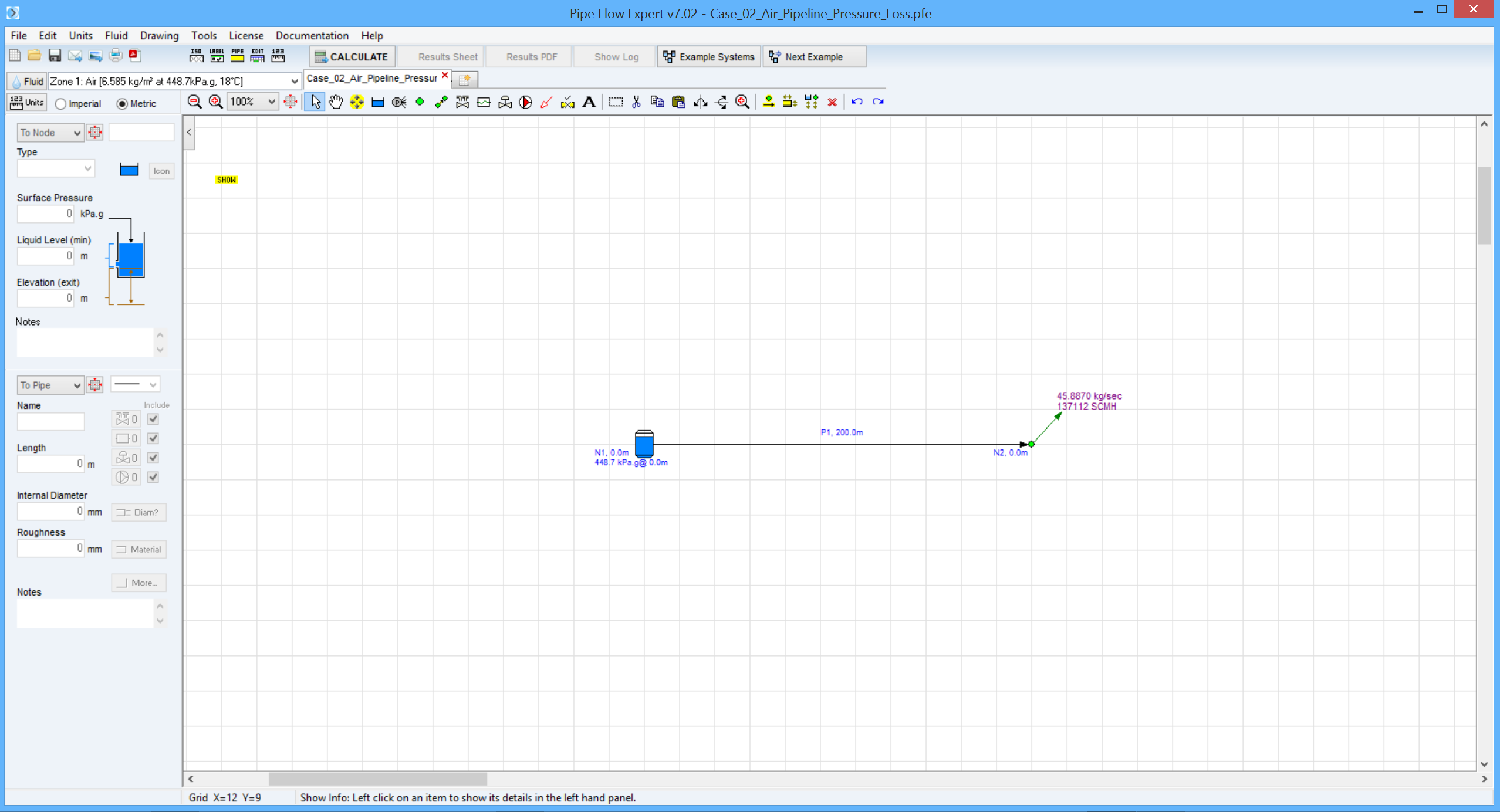
Pipe Flow Expert Parameters:
Fluid Data: Air at 18 °C, 0.0 kPa.g, viscosity 0.0181 centipoise.
Pipe Data: Used roughness 0.000001 mm (to give friction factor = 0.00802).
Flow rate: 45.887 kg/s (equivalent to 0.450 kN/s).
Calculation Method: Complete Isothermal Flow equation, Node Adjust Method.
Standard Atmospheric Model: 20°C, 101.325 kPa.
Gas Physical Model: Ideal Gas Law.
Result Comparison:
|
Data Item |
Published data |
Pipe Flow Expert |
|
Pressure 200m downstream (kPa.a) |
233 |
231.3 |
Commentary:
The published data and the calculated results compare well.
The published literature states the flow rate as a weight of flow in kN/s rather than as a gas flow at standard conditions. Kg/s = (kN/s) x (1000/g) (where g is acceleration due to gravity, normally 9.80665 m/s²). Hence a mass flow rate of 45.877 kg/s has been used in the calculation.

