Case 15: Natural Gas Looped Pipeline Inlet Pressure
Reference: Gas Pipeline Hydraulics, 2005, CRC Press, E. Shashi Menon, Chapter 3, page 118 Example 8
Pipe Flow Expert File: Case_15_Natural_Gas_Looped_Pipeline.pfe
Problem Description:
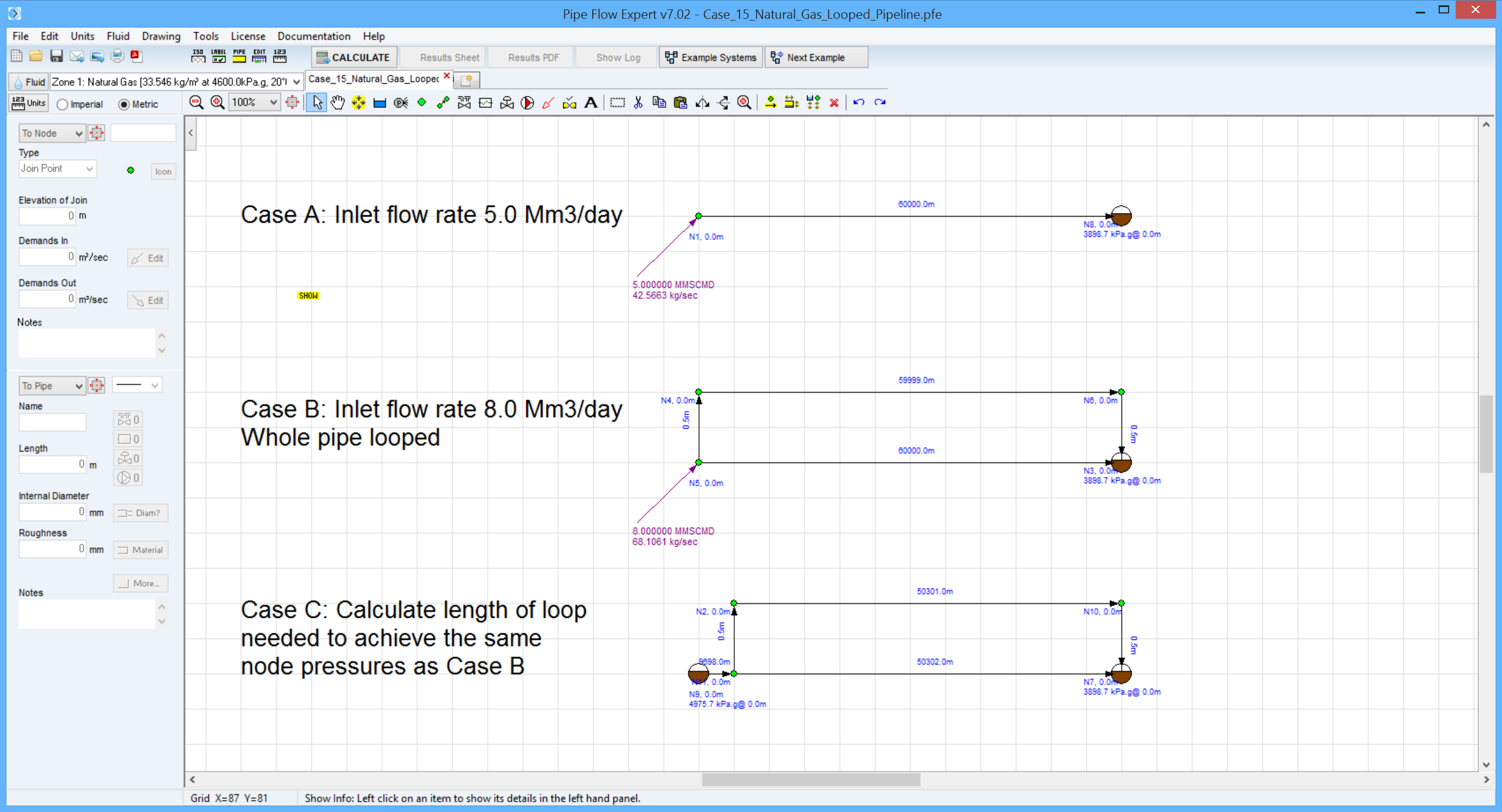
A natural gas pipeline, internal diameter 476 mm, is 60 km long.
The gas flow rate is 5.0 Mm3/day at 20 °C.
Calculate the inlet pressure required to achieve a delivery pressure of 4 MPa.a.
The pipe roughness is 0.015 mm.
Gas gravity is 0.65 and the compressibility factor is 0.88.
In order to increase the flow rate through the pipeline, the entire line is looped with pipe of internal diameter 476 mm.
Assuming the same delivery pressure, calculate the inlet pressure at the new flow rate of 8 Mm3/day.
If the inlet and outlet pressures are held the same as before, what length of the pipe should be looped to achieve the increased flow?
The calculation method used for the published data was the General Flow equation.
Fluid Data: Natural Gas with specific gravity 0.65 (0.783 kg/m3), 20 °C, 0.0 bar.g, viscosity 0.0119 centipoise.
Pipe Data: Absolute roughness 0.015 mm.
Calculation Method: General Isothermal Flow equation, Node Adjust Method.
Standard Atmospheric Model: 15°C, 101.325 kPa.
Gas Physical Model: Real Gas Model (Ideal Gas Law with compressibility factor Z=0.88).
Result Comparison:
|
Data Item |
Published data |
Pipe Flow Expert |
|
Inlet pressure (MPa absolute) flow rate = 5.0 Mm3/day |
5.077 |
5.077 |
|
Inlet pressure (MPa absolute) flow rate = 8.0 Mm3/day |
4.724 |
4.724 |
|
Length of pipe loop (km) |
48.66 |
48.66 |
Commentary:
The published data and the calculated results compare well. The target flow rate for the looped 48.66 km pipeline was 8 Mm3/day. The Pipe Flow Expert flow results for this looped model was 7.9978 MMSCMD (with an inlet pressure 5.077 MPa absolute, same as the 5.0 Mm3/day flow arrangement).

