Case 14: Methane Compressor to Processing Unit
Reference: Chemical Engineering Volume 1, 6th Ed, 1999, Elsevier, J M Coulson, J F Richardson, page 168 Example 4.3
Pipe Flow Expert File: Case_14_Methane_Compressor_Flow_Rate.pfe
Problem Description:
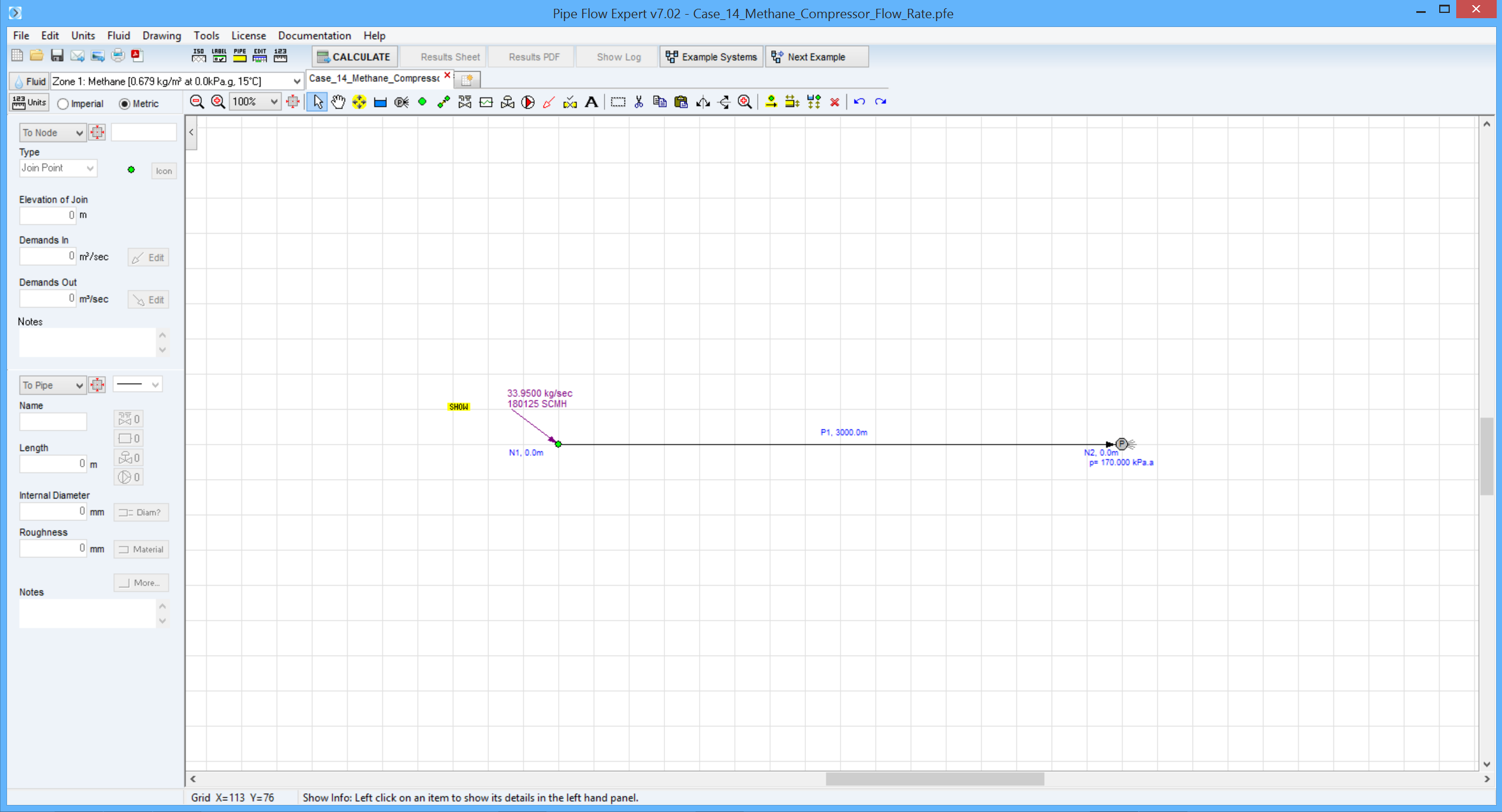
A flow of 50 m3/s methane at 288 K and 101.3 kN/m2 has to be delivered along a 0.6 m diameter line, 3.0 km long with a relative roughness of 0.0001, linking a compressor and a processing unit.
The delivery pressure is to be 170 kN/m2 and the delivery temperature 288 K.
The methane leaves the compressor at 297 K.
What pressure is needed at the compressor to achieve this flow rate?
The calculation method used for the published data was the Complete Isothermal equation.
Fluid Data: Methane at 293 K average, 0.00 kPa.g, density 0.667218 kg/m3, viscosity 0.0108 centipoise.
Pipe Data: Absolute roughness 0.06 mm.
Calculation Method: Complete Isothermal Flow equation, Node Adjust Method.
Standard Atmospheric Model: 15°C, 101.325 kPa
Gas Physical Model: Ideal Gas Law
Result Comparison:
|
Data Item |
Published data |
Pipe Flow Expert |
|
Compressor pressure (N/m2) |
405000 |
408198 |
Commentary:
The calculation method used was the Complete Isothermal equation.
The published data and the calculated results compare well.

