Case 17: Natural Gas Distribution Pipeline Looping
Reference: Gas Pipeline Hydraulics, 2005, CRC Press, E. Shashi Menon, Chapter 5, page 194 Example 3
Pipe Flow Expert File: Case_17_Natural_Gas_Distribution_Pipeline_Looping.pfe
Problem Description:
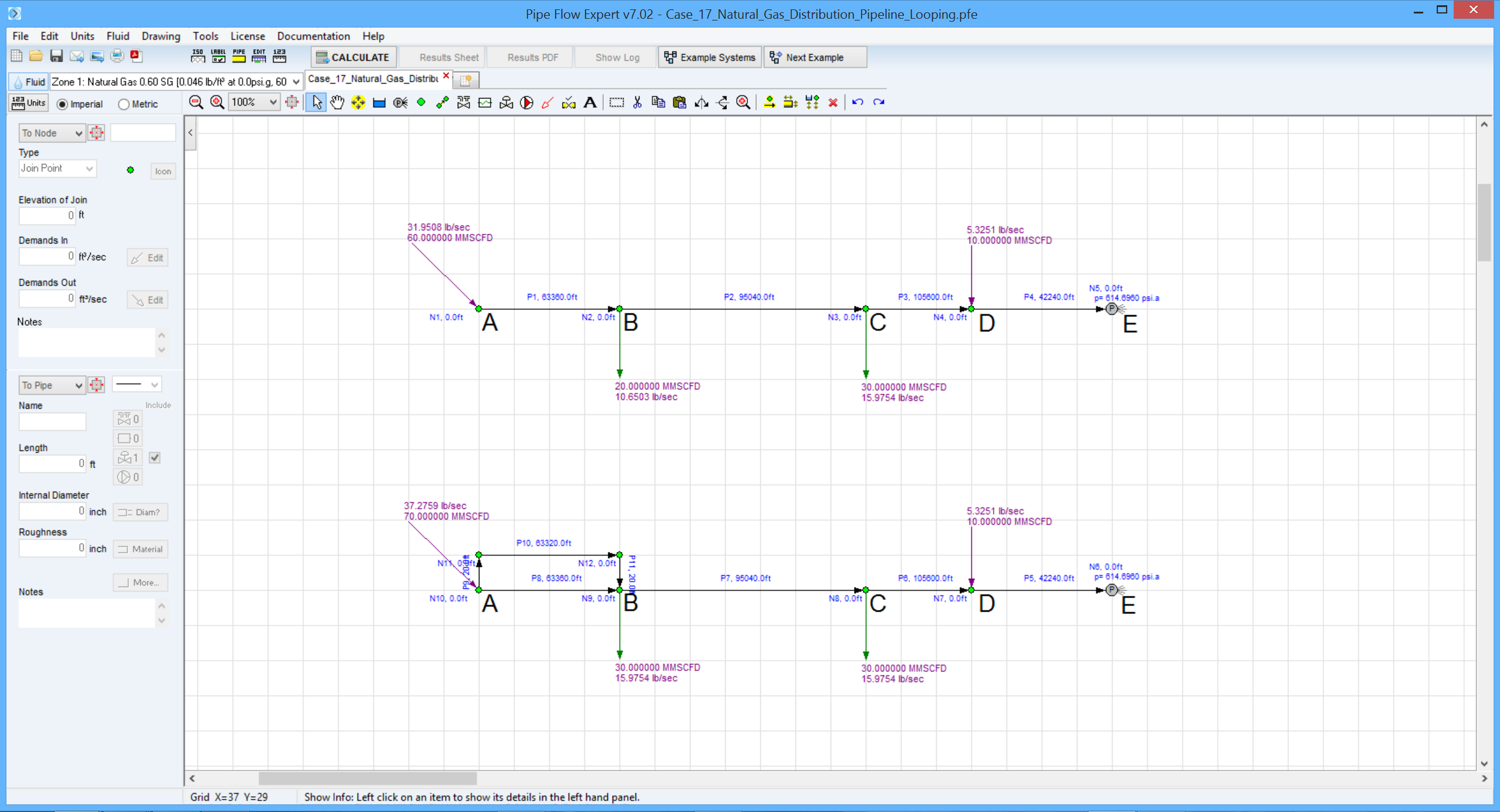
In a gas distribution pipeline, 60 MMSCFD enters the pipeline at A, as shown in the screen image below.
If the delivery at B is increased from 20 MMSCFD to 30 MMSCFD by increasing the inlet flow at A, keeping all downstream flow rates the same, calculate the diameter of looping pipe necessary for section AB to ensure pressures are not changed throughout the pipeline.
Assume the entire section AB is looped.
Pipe AB is 12 miles long with 13.5 inch internal diameter, BC is 18 miles long with 12.25 inch internal diameter, pipe CD is 20 miles long with 10.25 inch internal diameter and DE is 8 miles long with 12.25 inch internal diameter.
The delivery pressure at E is fixed at 600 psi.g.
The gas gravity is 0.6 and the flow temperature is 60 °F. Compressibility factor is 0.85.
The calculation method used for the published data was the General Flow Equation.
Fluid Data: Natural Gas with specific gravity 0.6, 60 °F (0.046 lb/ft3), viscosity 0.0119 centipoise.
Pipe Data: Absolute roughness 0.000250 inches.
Calculation Method: General Isothermal Flow equation, Node Adjust Method.
Standard Atmospheric Model: 60°F, 14.696 psi
Gas Physical Model: Real Gas Model (Ideal Gas Law with compressibility factor Z=0.85).
Result Comparison:
|
Data Item |
Published data |
Pipe Flow Expert |
|
Pressure at A (psi abs) for initial flow rate |
677.45 |
680.64 |
|
Pressure at B (psi abs) for initial flow rate |
651.90 |
654.85 |
|
Internal diameter of looped pipe (inches) |
6.6 |
6.8 |
Commentary:
The published data and the calculated results compare well.
The published data used a transmission factor of 20 instead of a roughness value for the pipe. We have used a roughness value of 0.00025 inches which gives friction factors around 0.01, which is equivalent to a transmission factor of 20.

