Case 20: Flow of Natural Gas through Steel Pipe
Reference: Flow of Fluids through Valves, Fittings and Pipe Metric Edition – SI Units, Crane Technical Paper 410M, page 3-18 Example 1
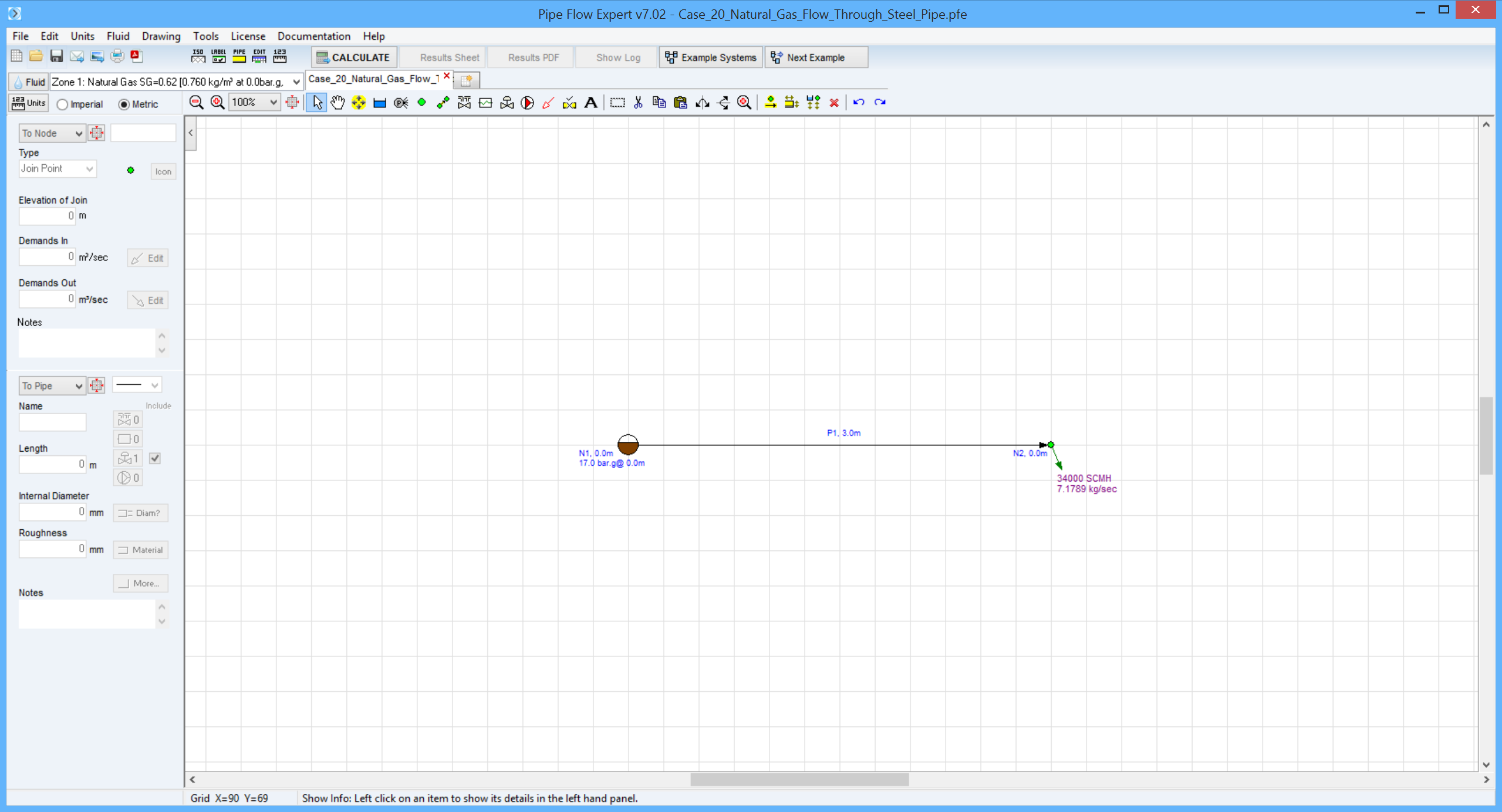
Pipe Flow Expert File: Case_20_Natural_Gas_Flow_Through_Steel_Pipe.pfe
Problem Description:
Natural Gas at 17 bar gauge and 15° C with a specific gravity of 0.62, flows through a steel pipe 200 mm inside diameter at a rate of 34 000 standard cubic metres per hour.
Find the flow rate in kilograms per hour, the Reynolds number and the friction factor.
The calculation method used for the published data was the Darcy-Weisbach equation.
Fluid Data: Natural Gas at 15 °C, specific gravity 0.62, 0.0 bar.g, density 0.760 kg/m3, viscosity 0.0120 centipoise.
Pipe Data: Roughness 0.046 mm (pipe material Steel (ANSI) schedule 40).
Calculation Method: General Isothermal Flow equation, Node Adjust Method.
Standard Atmospheric Model: 15°C, 0.0 bar.g
Gas Physical Model: Ideal Gas Law
Result Comparison:
|
Data Item |
Published data |
Pipe Flow Expert |
|
Mass Flow (kg/hour) |
26000 |
25844 |
|
Reynolds Number |
4000000 |
3808539 |
|
Friction Factor |
0.014 |
0.014369 |
Commentary:
The published data and the calculated results compare well.
Pipe Flow Expert calculated the friction factor more accurately and displayed it to six decimal places.
Using a more accurate friction factor produces a slightly difference result, as shown above.

