Case 21: Air Pressure Drop in Steel Pipe
Reference: Piping Calculations Manual, 2005, McGraw-Hill, E. Shashi Menon, Chapter 5, page 265 Example 5.8
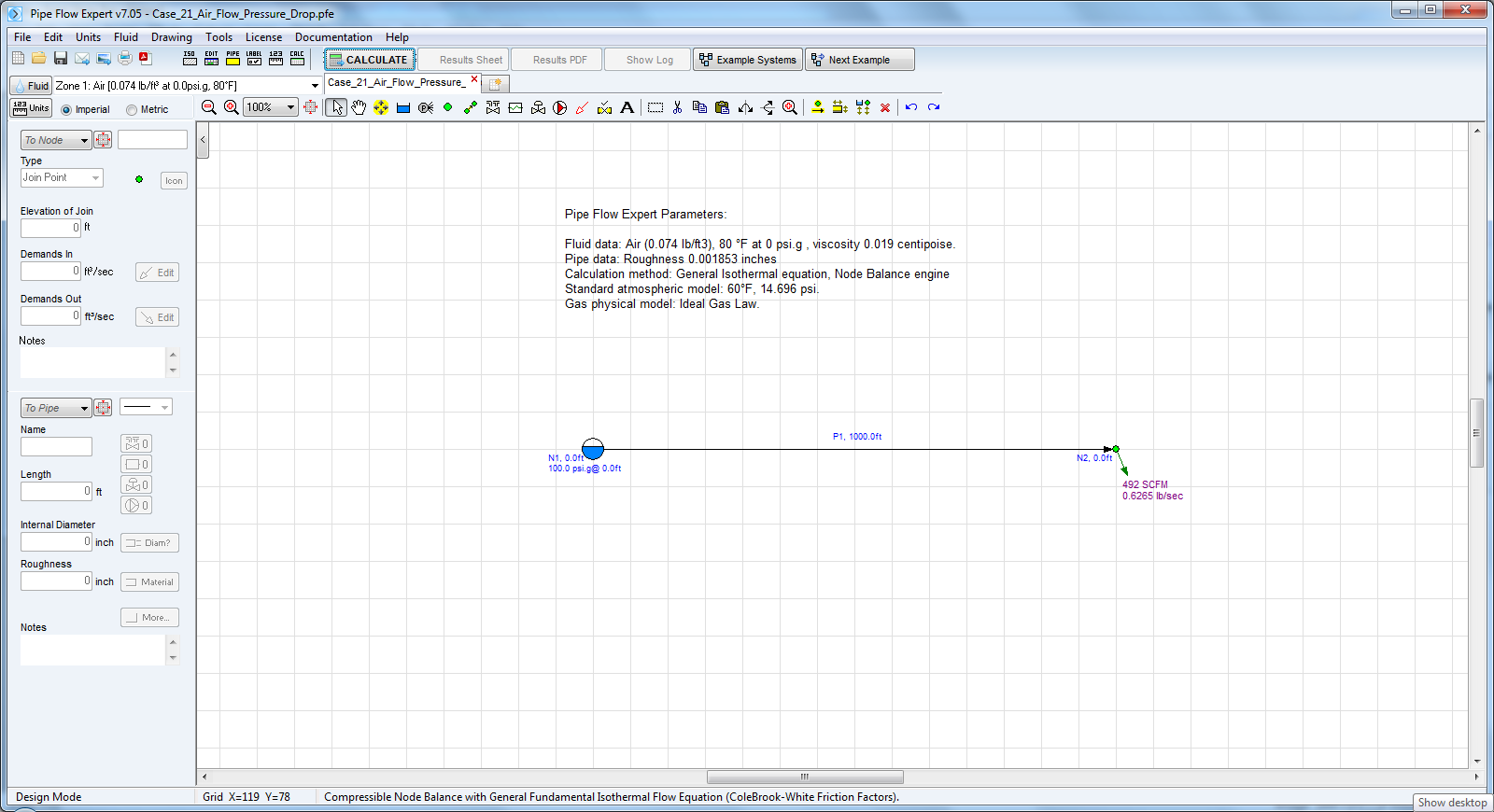
Pipe Flow Expert File: Case_21_Air_Flow_Pressure_Drop.pfe
Problem Description:
Air flows at 50 ft/s in a 2” inside diameter pipe at 80°F, at an initial pressure of 100 psi.g.
If the pipe is horizontal and 1000 ft long, calculate the pressure drop if the flow is isothermal.
Use a friction factor of 0.02.
The calculation method used for the published data was the General Isothermal Flow Equation.
Fluid Data:
|
Air at 80 °F, 0.0 bar.g, density 0.0736 lb/ft3, viscosity 0.0185 centipoise. |
|
Pipe Flow Expert will automatically calculate for compression of the gas to the 100 psi.g condition. |
|
The fluid data must however be defined at the required temperature. |
Pipe Data: Roughness 0.001853 inches (pipe material Steel (ANSI) schedule 40).
Calculation Method: General Isothermal Flow equation, Node Adjust Method.
Standard Atmospheric Model: 60°F, 14.696 psi.a
Gas Physical Model: Ideal gas Law.
Result Comparison:
|
Data Item |
Published data |
Pipe Flow Expert |
|
Outlet Pressure (psi.a) |
94.18 |
94.1782 |
|
Pressure drop (psi) |
20.52 |
20.5178 |
Commentary:
The published data and the calculated results compare well.
The normal pipe roughness for mild steel pipe is 0.001811 inches, however this was adjusted to 0.001853 inches to give a friction factor of 0.02 as assumed in the published text.
Although the fluid data is defined for 80°F and 0.0 bar.g, Pipe Flow Expert’s compressible flow engine automatically accounts for and calculates for compression of the air down to the 100 psi.g starting condition.

