Case 22: Natural Gas Flow Rate vs Pressure Drop In Steel Pipe
Reference: Fluid Flow Handbook, 2002, McGraw-Hill, Jamal M. Saleh, Ph D., PE, Chapter 9, page 9.14 Ex. 9.5.1
Pipe Flow Expert File: Case_22_Diameter_of_Pipeline_78_miles_long.pfe
Problem Description:
Find the inside diameter of a steel pipe used to transport natural gas (SG = 0.87) a distance of 78 miles when the following requirements are specified.
The inlet pressure is 600 psi.g and the maximum allowable pressure drop is 145 psi.g.
Assume isothermal flow and a pipeline efficiency of 0.92
The compressibility factor Z = 0.8337 (calculated from Papay’s correlation)
The calculation method used for the published data was the Panhandle B equation.
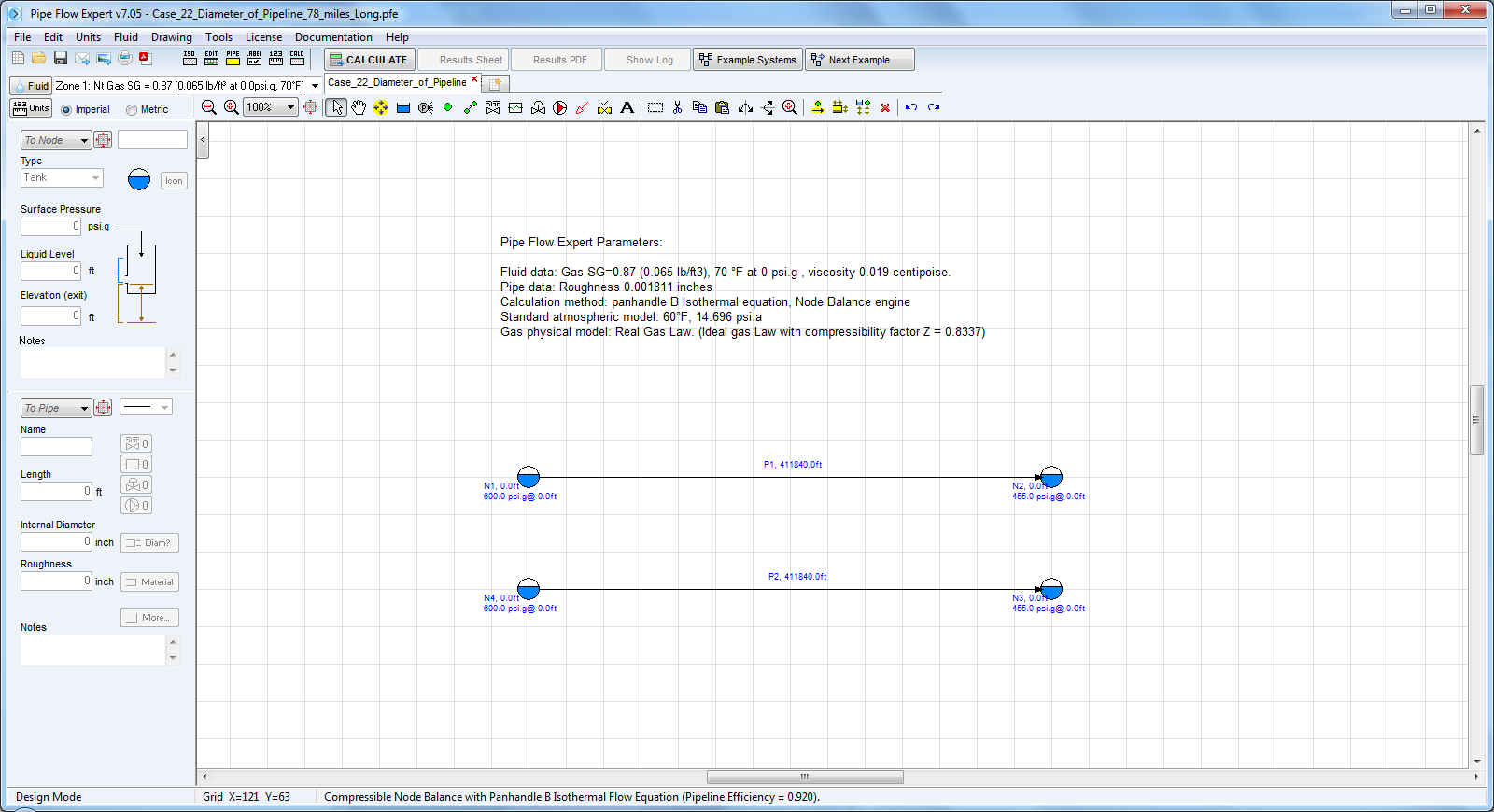
Fluid Data: Natural Gas at 70 °f, 0.0 psi.g, density 0.650 lb/ft3, viscosity 0.0119 centipoise
Pipe Data: Internal diameter 18.812 inches (nominal 20” diameter), roughness 0.001811 inches (pipe material Steel (ANSI) schedule 40).
Calculation Method: Panhandle B Isothermal equation, Node Adjust Method.
Standard Atmospheric Model: 60°F, 14.696 psi.a
Gas Physical Model: Real Gas Model (Ideal Gas Law with compressibility factor Z=0.8337).
Result Comparison:
|
Data Item |
Published data |
Pipe Flow Expert |
Pipe Flow Expert; Flow Rate |
|
Inner diameter |
18.80 inches |
18.800 inches |
100.049 MMSCFD |
|
20” nominal diameter |
N/A |
18.812 inches |
100.211 MMSCFD |
Commentary:
The published data and the calculated results compare well.
A supplementary calculation using a nominal 20 inch Steel pipe (schedule 40) with an 18.812 inch inner diameter confirms a similar flow rate within the allowed 145 psi.g pressure drop.

