Case 24: Air Flowing through Horizontal Pipe
Reference: Elementary Fluid Mechanics, 1940, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., John K. Vennard, page 163 “Illustrative Problem”
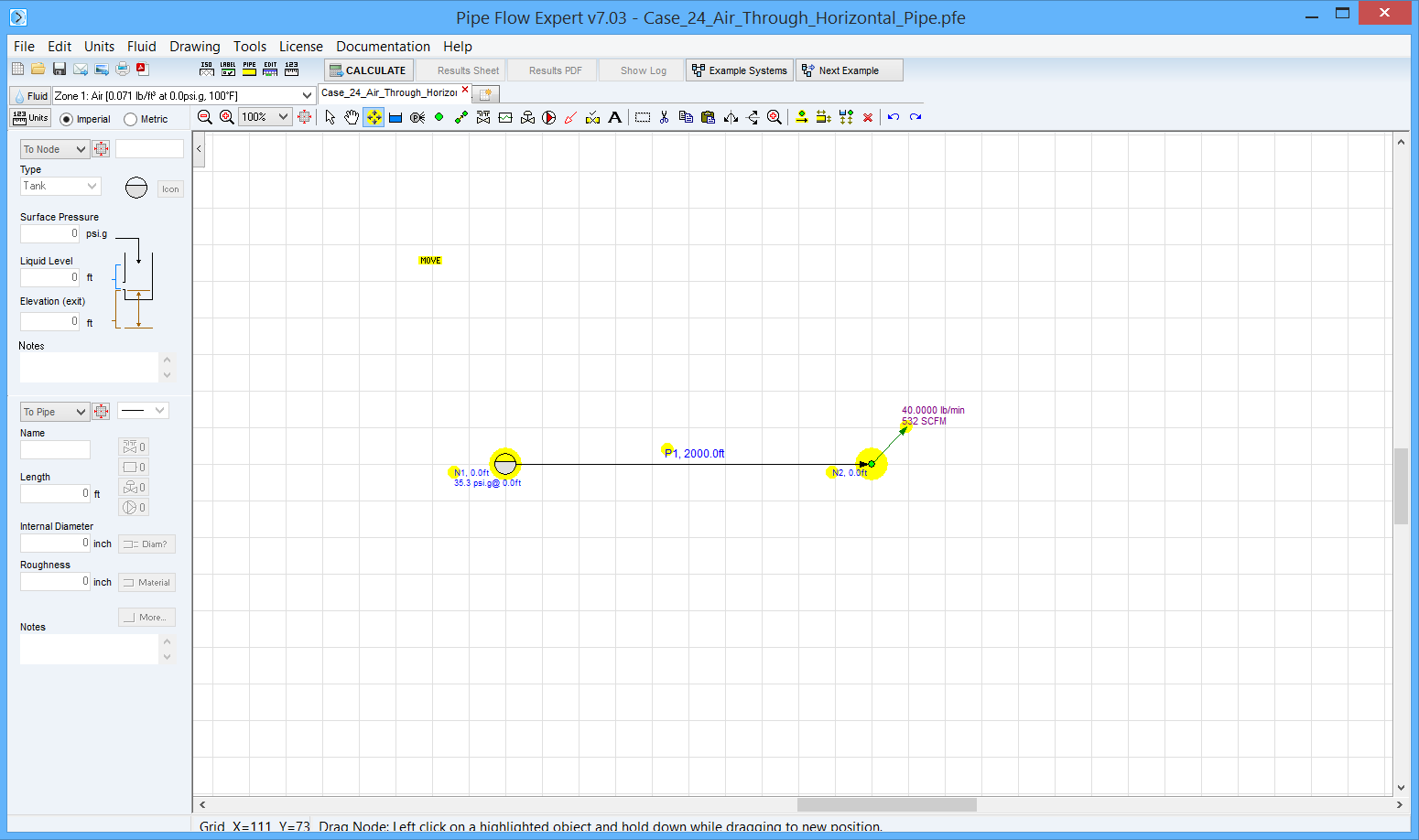
Pipe Flow Expert File: Case_24_Air_Through_Horizontal_Pipe.pfe
Problem Description:
Air is pumped from a reservoir at 50 psi.a through a clean horizontal smooth pipe 3” in diameter and 2000 ft long.
The conditions of flow are isothermal and the temperature of the gas is 100 degrees F.
With a flow rate of 40 lb/min what is the pressure 2000 ft downstream?
The calculation method used for the published data was the Simplified version of the Complete Isothermal Equation, which neglects the term 2*ln(V2/V1) since this is normally small compared to f*(L/D).
Fluid Data: Air at 100 °F, 0.0 psi.g, density 0.071 lb/ft3, viscosity 0.0191 centipoise.
Pipe Data: Internal diameter 3 inches, roughness 0.000001 inches.
Calculation Method: Complete Isothermal Flow equation, Node Adjust Method.
Standard Atmospheric Model: 68 °F, 14.696 psi absolute.
Gas Physical Model: Ideal Gas Law
Result Comparison:
|
Data Item |
Published data |
Pipe Flow Expert |
|
Pressure 2000 feet downstream |
39.3 psi.a |
38.96 psi.a |
|
Friction factor |
0.0145 |
0.014818 |
Commentary:
The published data and the calculated results compare well.
The published result was calculated using a friction factor of 0.0145 (which was read from a plot).
Pipe Flow Expert used a pipe roughness of 0.000001 inches, calculating a friction factor of 0.0148.

