Case 40: Air - Pressure Loss Due to Mass Flow Rate
Reference: Piping Calculations Manual, 2005, McGraw-Hill, E. Shashi Menon, P.E., Page 265, Example 5.8
Pipe Flow Expert File: Case_40_Air_Pressure_Loss_Due_To_Mass_Flow_Rate.pfe
Problem Description:
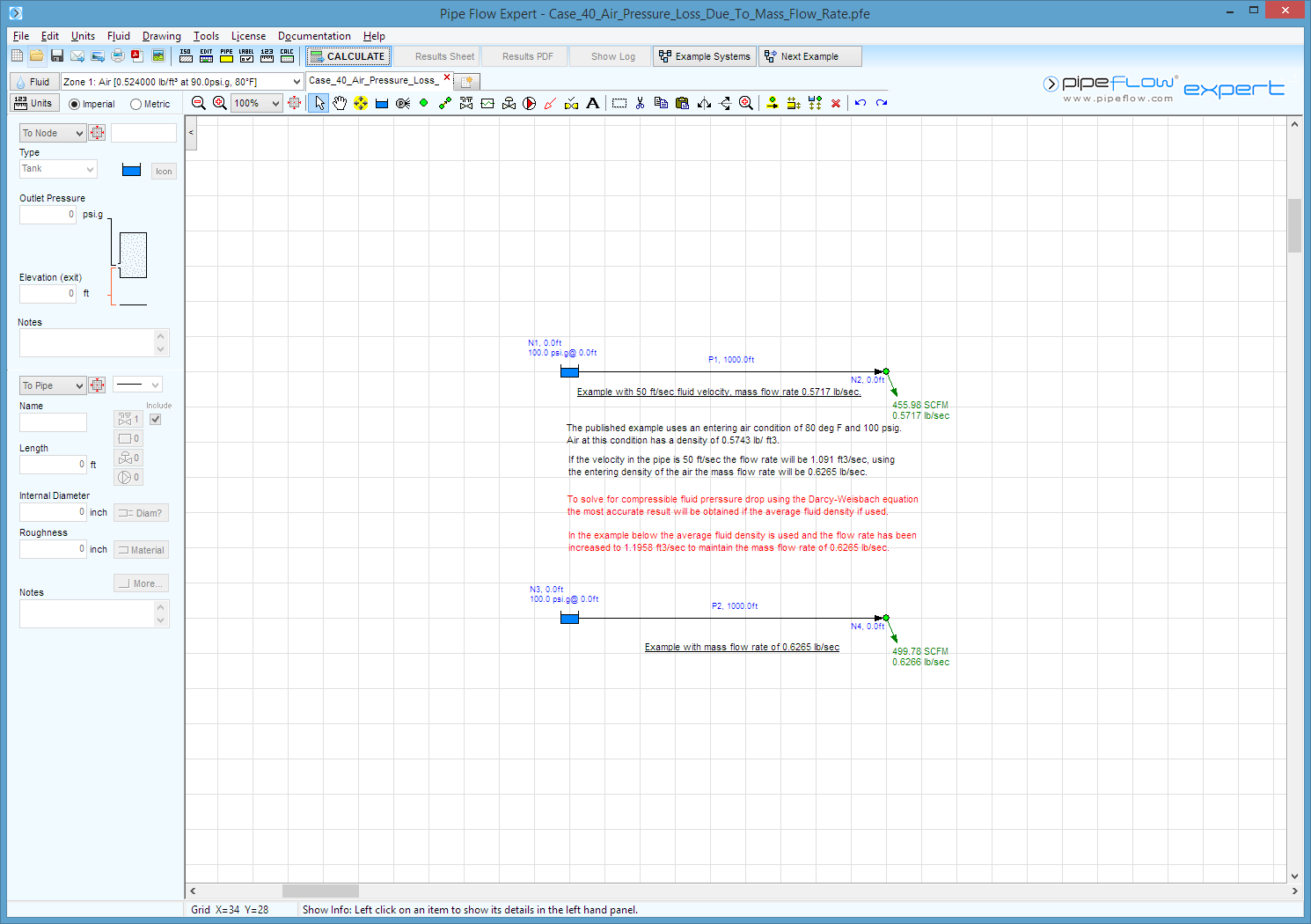
Air at temperature of 80°F and a pressure of 100 psig flows into a steel pipe with 2” internal diameter.
The initial velocity of the air is 50 ft/sec.
The flow is isothermal.
The pipe is horizontal and 1000 ft long.
Calculate the pressure loss in the pipe.
Note: This case is solved here using Pipe Flow Expert’s non-compressible calculation engine. See the commentary below for more details.
This case has also been solved using Pipe Flow Expert’s compressible calculation engine and the results are reported in the separate Compressible Results Verification document (Case 21).
Fluid Data: Air at 80°F at an average density of 90 psig
Result Comparison:
|
Data Item |
Published data |
Pipe Flow Expert |
|
Pressure Loss (psi) |
20.52 |
20.3626 |
|
Weight of Flow (lb/sec) |
0.6265 |
0.6266 |
|
Friction Factor |
0.020 |
0.01988 |
Commentary:
The published data and the calculated results compare well.
The weight of flow is calculated from the fluid data and the initial velocity as 0.6265 lb/sec.
The published text assumes an initial friction factor of 0.020 this is used together with the mass flow rate to estimate the fluid pressure at the end of the pipe.
A further iteration involving the new fluid pressure at the end of the pipe provides the published result.
The average density of the air has been used in the Pipe Flow Expert Calculation.
The Pipe Flow Expert program uses the Darcy-Weisbach equation to determine flow rates and pressure loss in pipes.
Where the system includes compressible fluids and the pressure loss is greater than 10% of the entering pressure the calculations need to be carried out using the average fluid density to obtain an accurate result.
In order to maintain the flow rate of 0.6265 lb/sec the flow rate in the pipe has been adjusted to use the average flow velocity that will be present in the pipe.
Normally Pipe Flow Expert would be used with the Compressible Flow calculation engine to analyze this system.

