Case 05: Gas Pipeline Inlet Pressure
Reference: Gas Pipeline Hydraulics, 2005, CRC Press, E. Shashi Menon Chapter 2, page 67 Example 16
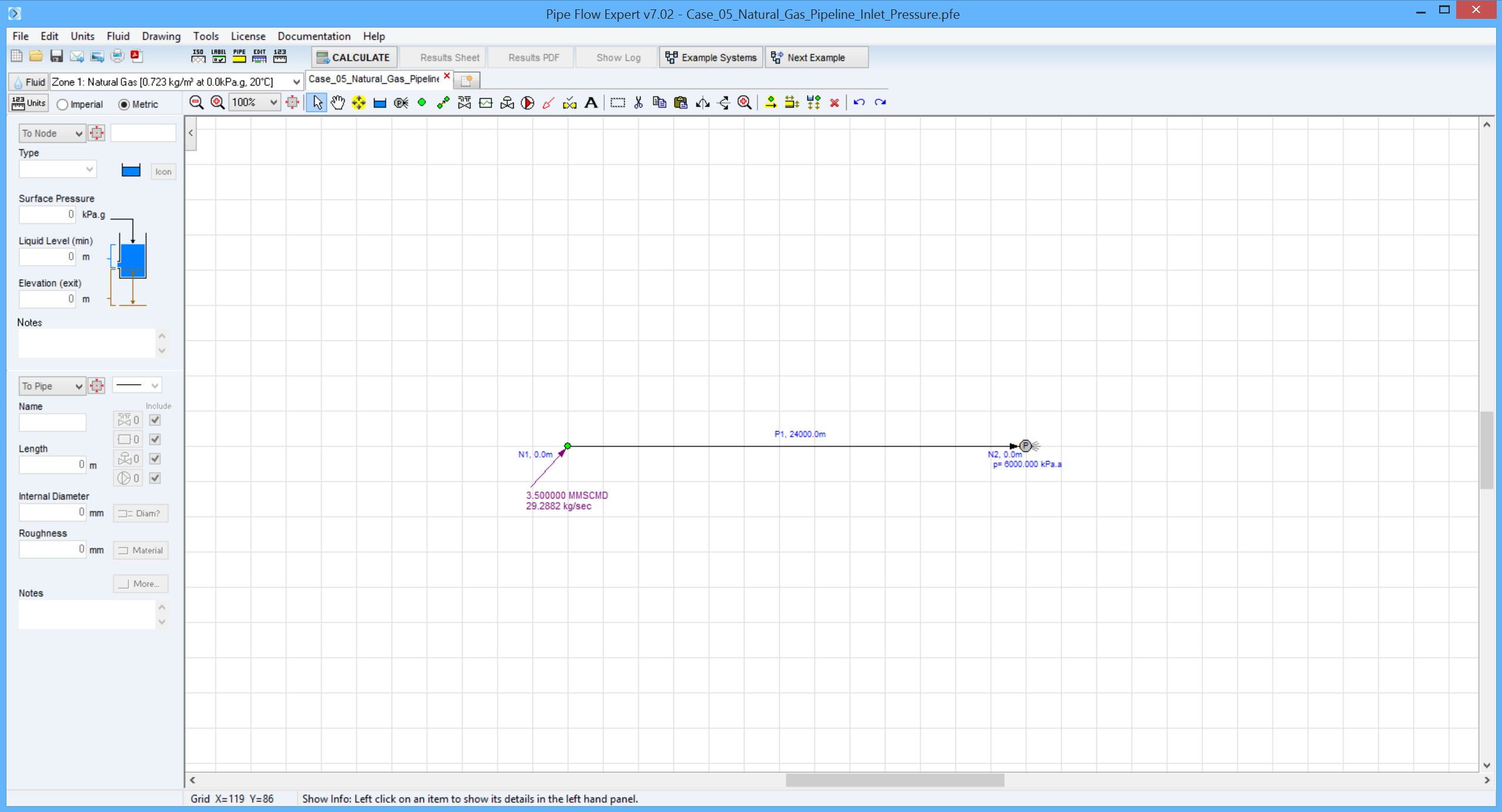
Pipe Flow Expert File: Case_05_Natural_Gas_Pipeline_Inlet_Pressure.pfe
Problem Description:
Calculate the inlet pressure in a 24 km natural gas pipeline, with internal diameter 288 mm.
The gas flow rate is 3.5 Mm3/day and the delivery pressure is 6000 kPa absolute.
The average gas temperature is 20 °C, the pipeline efficiency is 0.92 and the gas compressibility factor is 0.90.
The calculation method used for the published data was the Panhandle A equation.
Pipe Flow Expert Parameters:
Fluid Data: Gas specific gravity 0.6 (0.723 kg/m3), 20 °C, 0.00 kPa.g, viscosity 0.0119 centipoise.
Pipe Data: Pipeline efficiency = 0.92.
Flow Rate: 3.5 MMSCMD.
Calculation Method: Panhandle A Isothermal equation, Node Adjust Method.
Standard Atmospheric Model: 15 °C, 101.325 kPa.
Gas Physical Model: Real Gas Model (Ideal Gas Law with compressibility factor Z=0.9).
Result Comparison:
|
Data Item |
Published data |
Pipe Flow Expert |
|
Inlet pressure (kPa absolute) |
7471 |
7480 |
Commentary:
The published data and the calculated results compare well.
The publication states the gas flow rate is 3.5 Mm3/day. Here, the ‘M’ stands for ‘one million’, which is not the same as the ‘M’ in “standard condition” units i.e. MSCMD. In “standard condition” units a single ‘M’ stands for ‘one thousand’, and ‘MM’ stands for one million.

